Application
Overview
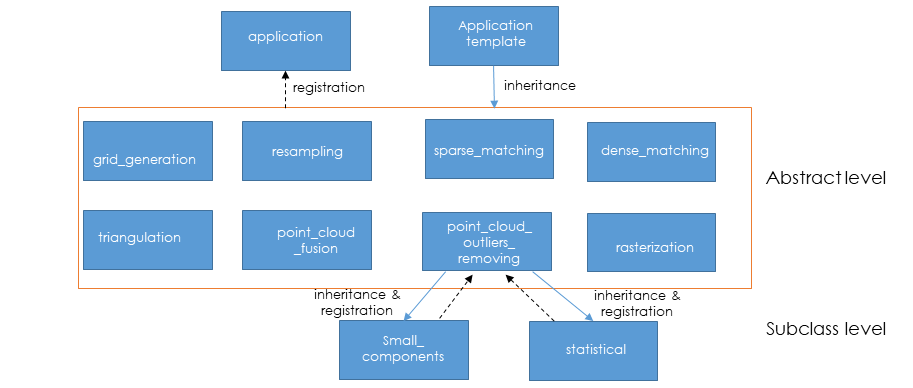
An application is a main step of CARS 3D reconstruction framework. It contains algorithm methods. It takes CarsDatasets and configuration parameters as input and returns CarsDatasets.
It is composed of: * an application factory concept that register all 3D step application * an application template * Some abstract applications (each one defined a main 3d step) * Some subclass associated to each abstract application, containing specific algorithm
Example
Let’s take an example of dense_matching application to describe the main steps:
First, we can notice that dense_matching derives from ApplicationTemplate and is registered with the decorator:
@Application.register("dense_matching")
class DenseMatching(ApplicationTemplate, metaclass=ABCMeta):
Then, algorithm is contain in a subclass register, by is short_name, of dense_matching application.
class CensusMccnnSgm(
DenseMatching, short_name=["census_sgm"]
)
Init with parameters checking
To instantiate, need the orchestrator and a configuration file that contains algorirhm parameters.
def __init__(self, orchestrator, conf_matching):
"""
Init function of DenseMatching
:param orchestrator: orchestrator used
:param conf_matching: configuration for matching
:return: a application_to_use object
"""
# orchestrator
self.orchestrator = orchestrator
# check conf
self.corr_config = None
if "corr_config" in conf_matching:
self.corr_config = conf_matching["corr_config"]
# For now, this is a path, transform it to dict
# later : integrated to input config
# TODO use loader to check and generate corr_config
self.corr_config = corr_conf.configure_correlator(self.corr_config)
self.correlator = None
if "correlator" in conf_matching:
self.correlator = conf_matching["correlator"]
else:
self.correlator = "pandora"
# check loader
# Saving files
if "save_disparity_map" in conf_matching:
self.save_disparity_map = conf_matching["save_disparity_map"]
else:
self.save_disparity_map = False
#
Run,Take CarsDataset as input and return new CarsDatasets.
def run(
self,
epipolar_images_left,
epipolar_images_right,
pair_folder,
):
"""
Run Matching application.
Create left and right CarsDataset filled with xarray.Dataset ,
corresponding to epipolar disparities, on the same geometry
that epipolar_images_left and epipolar_images_right.
:param epipolar_images_left: tiled left epipolar
:type epipolar_images_left: CarsDataset
:param epipolar_images_right: tiled right epipolar
:type epipolar_images_right: CarsDataset
:param pair_folder: folder used for current pair
:type pair_folder: str
:return Disparity map
:rtype: CarsDataset
"""
2.1. Create empty CarsDatasets.
if epipolar_images_left.dataset_type == "arrays":
# Create CarsDataset
# Epipolar_disparity
epipolar_disparity_map = cars_dataset.CarsDataset("arrays")
epipolar_disparity_map.create_empty_copy(epipolar_images_left)
# Update attributes to get epipolar info
epipolar_disparity_map.attributes.update(
epipolar_images_left.attributes
)
2.2 Declare to Orchestrator which products we want to save.
# Save disparity maps
if self.save_disparity_map:
self.orchestrator.add_to_save_lists(
os.path.join(pair_folder, "epi_disp.tif"),
cst_disp.MAP,
epipolar_disparity_map,
)
....
2.3 Ask to the Orchestrator ID for each CarsDataset
# Get saving infos in order to save tiles when they are computed
[
saving_info
] = self.orchestrator.get_saving_infos(
[epipolar_disparity_map]
)
2.4 Tile by tile, algorithm step computation
Use create_task function of the cluster throughout the Orchestrator. Algorithm function is called. See juste above
create_task returns a delayed stored in previous created CarsDataset
# Generate disparity maps
for col in range(epipolar_disparity_map.shape[1]):
for row in range(epipolar_disparity_map.shape[0]):
# Compute disparity
(
epipolar_disparity_map[row, col],
) = self.orchestrator.cluster.create_task(
compute_disparity
)(
epipolar_images[row, col],
self.corr_config,
saving_info=saving_info,
)
else:
logging.error(
"DenseMatching application doesn't "
"support this input data format"
)
return epipolar_disparity_map
For each tile, the core algorithm function is called.
Takes unique tile in input (not a whole CarsDataset) and returns a tile
Add the ID, given by orchestrator, to this tile
def compute_disparity(
image_object: xr.Dataset,
corr_cfg: dict,
saving_info=None,
) -> Dict[str, xr.Dataset]:
"""
Compute disparity map from image objects.
This function will be run as a delayed task.
User must provide saving infos to save properly created datasets
:param left_image_object: tiled Left image
* dataset with :
- cst.EPI_IMAGE
- cst.EPI_MSK (if given)
- cst.EPI_COLOR (for left, if given)
:type left_image_object: xr.Dataset
* dataset with :
- cst.EPI_IMAGE
- cst.EPI_MSK (if given)
- cst.EPI_COLOR (for left, if given)
:param right_image_object: tiled Right image
:type right_image_object: xr.Dataset
:param corr_cfg: Correlator configuration
:type corr_cfg: dict
:returns: Disparity object
Returned objects are composed of :
* dataset with :
- cst_disp.MAP
- cst_disp.VALID
- cst.EPI_COLOR
"""
# Get disp_min and disp_max
disp_min = cars_dataset.get_attributes(left_image_object)["disp_min"]
disp_max = cars_dataset.get_attributes(left_image_object)["disp_max"]
# Compute disparity
disp = dense_matching_tools.compute_disparity(
left_image_object,
right_image_object,
corr_cfg,
disp_min,
disp_max,
mask1_ignored_by_corr=mask1_ignored_by_corr,
mask2_ignored_by_corr=mask2_ignored_by_corr,
)
# Fill with attributes
left_disp_dataset = disp[cst.STEREO_REF]
cars_dataset.fill_dataset(
left_disp_dataset,
saving_info=saving_info_left,
window=cars_dataset.get_window_dataset(left_image_object),
profile=cars_dataset.get_profile_rasterio(left_image_object),
attributes=None,
overlaps=None, # overlaps are removed
)
return disp_dataset
At the end of the application, we can obtain CarsDatasets filled with delayed, one per tile.